In the production of cast rods, there are defects such as inclusions, segregation, cracks, pores, and porosity. The more serious defects are inclusions, cracks and feather-like crystals. Therefore, under the existing equipment conditions, how to make the quality inclusion defects of the products get effective control is the key to aluminum alloy casting production.

Causes of Inclusions
The inclusions in the cast rods are mainly non-metallic slags, such as metal oxides Al2O3, MgO, smelting furnace refractory particles, nitrides produced during melt purification, and debris on launders and tools. These inclusions are extremely unevenly distributed, with different sizes and shapes, which seriously affect the continuity of texture and lay hidden dangers for the subsequent processing of waste products. The main reasons for their occurrence are as follows:
Incomplete refining and slag removal of aluminum melt causes inclusions
Since the electrolytic aluminum liquid contains non-metallic salt impurities such as cryolite and alumina, the waste material added during the batching process contains more oxide film, and the failure to clean the furnace in time will cause pollution to the aluminum liquid. If the refining is not thorough, the refining temperature, the standing temperature and the standing time are unreasonable, the effect of the refining agent and coating used in the melt purification treatment is not good, and the product will be mixed.
Irregular operation causes inclusions
During the casting process, the operating tools were not clean, the pouring system was not cleaned, and other reasons, which caused the aluminum liquid to be contaminated again, and impurities were brought into the melt during pouring to cause inclusions. In addition, since the surface of molten aluminum is easy to form a dense oxide film, the molten aluminum flows from the discharge port of the aluminum melting furnace to the launder, filter box, distributor, and crystallizer, forming a pouring system that seals the mass. Ensure the purification effect of molten aluminum. If the pouring flow is improperly controlled, the flow fluctuates, and the fluid is not stable, it will inevitably cause continuous damage to the oxide film on the surface of the pouring system and be involved in the melt, forming alumina inclusions.
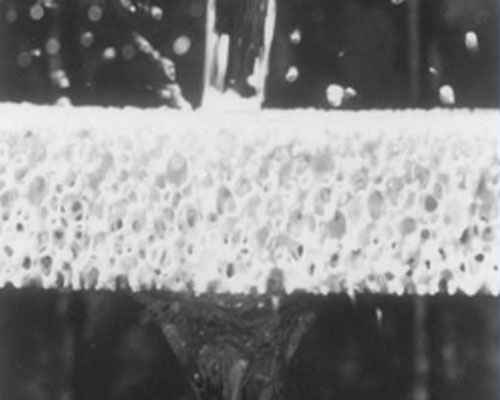

How to Control Inclusion
Pour the electrolytic aluminum liquid into the aluminum melting furnace steadily. The added solid materials must be strictly inspected. There is no mud, sand, water, oil, etc., and the feeding operation must be gently pushed. To avoid damage to the bottom of the furnace caused by the feeding of materials, the furnace should be cleaned once per shift, and the furnace should be cleaned thoroughly. The scum in the furnace must be removed every time the ingredients are mixed.
The refining of the melt is the key to eliminating inclusions. The refining temperature of the melt is controlled at 730~750℃, the standing time is 20~30min, high-quality refining agent is used, and the single solvent refining is changed to nitrogen spray refining flux improves the refining effect.
All operating tools must be kept dry and clean. Try to make the molten aluminum into the crystallizer smoothly during casting to avoid the molten aluminum from impacting the surface oxide film, causing the oxide film to be damaged and involved in the aluminum melt, forming new oxide inclusions.
The foam ceramic filter is filtered from the original filter plate surface at 45 degrees to the horizontal plane to be parallel to the horizontal plane. The aluminum liquid is filtered from top to bottom by its own weight to improve the CFF filtering effect.