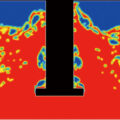
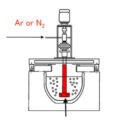
Gas purifier purification refers to the introduction of gas into the aluminum melt or the substances that can produce purified gas. The partial pressure difference between the hydrogen in the aluminum melt and the bubble is used to make it diffuse into the bubble, and the bubble captures the inclusion scum, etc. in the process of floating, so as to achieve the purpose of hydrogen and impurity removal. The main purpose of gas purifiers is to remove hydrogen. At the same time, because the impurities in the melt interact with hydrogen, the process of removing hydrogen is accompanied by impurity removal.
The aluminum purification effect of gas purifier is based on the theory of bubble floatation. According to the activity classification of gas purifiers, it can be divided into three categories: inert gas, active gas and oxidizing gas.
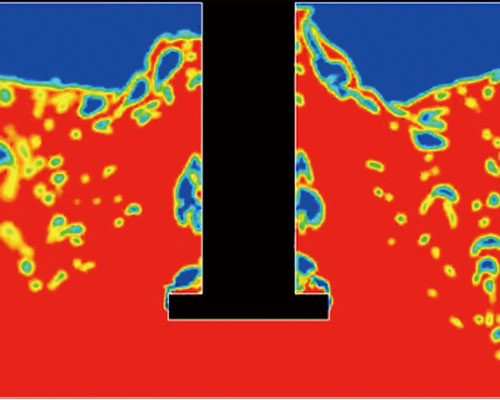
Inert gas refers to the gas that does not chemically react with aluminum melt and dissolved hydrogen, and is insoluble in aluminum, mainly Ar, N2, He, etc. They are non-toxic, tasteless and pollution-free, and do not require waste gas treatment facilities, and they can physically adsorb and remove hydrogen from the aluminum melt.
Active gas mainly refers to Cl2, in addition to ZnCl, MnCl, C2Cl6, CCl4 and other chlorine salts or chlorides produced in the purification process. Cl2 itself is insoluble in aluminum, but chlorine gas reacts with aluminum and hydrogen dissolved in aluminum. The reaction products HCl and AlCl3 are both gaseous and insoluble in molten aluminum. Initially, the hydrogen partial pressure in the AICl3 bubble is zero, thereby removing the hydrogen in the melt. The active gas has both physical and chemical hydrogen removal effects on the aluminum melt. But because it is harmful to human body, pollutes the environment, it is easy to corrode equipment and heating elements, and it is easy to make the crystal structure of alloy ingot coarse. Therefore, in order to avoid public hazards, people mostly use inert gas.
Oxidizing gas refers to the gas generated by the decomposition of the flux under the action of high temperature or the reaction with the aluminum melt, which is a newly developed flux method. But because it actually generates NO, NO2, CO, and HF gases that can violently oxidize the aluminum melt during the purification process.