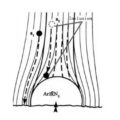
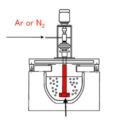
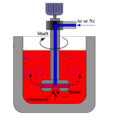
The floatation method is generally used for degassing. The principle is to pass a certain non-hydrogen-free gas into the aluminum liquid to generate bubbles, and use these bubbles to take the dissolved hydrogen out of the aluminum liquid and escape into the atmosphere during the floating process. In order to obtain a better refining effect, the iron pipe that introduces the gas should be pressed into the depth of the molten pool as much as possible, and the lower end of the iron pipe is 100mm~150mm away from the bottom of the crucible, so as to lengthen the upward stroke of the bubbles and at the same time not sink to the aluminum The inclusions at the bottom of the liquid stirred up.

Floatation Degassing Method
When the gas is introduced, the iron pipe should be moved slowly and laterally in the molten aluminum so that there are bubbles passing through the molten pool. Try to use a lower ventilation pressure and speed, because the bubbles formed in this way are smaller, which enlarges the surface area of the bubbles, and because the bubbles are small, the floating speed is also slow, which can remove more inclusions and gases.
At the same time, in order to ensure a good refining effect, the selection of the refining temperature should be appropriate. If the temperature is too high, the bubbles generated will be larger and will rise quickly, making the refining effect worse. When the temperature is too low, the viscosity of the molten aluminum is large, which is not conducive to the full discharge of the gas in the molten aluminum, and also reduces the refining effect.
Ultrasonic treatment of molten aluminum can also effectively degas. Its principle is that by introducing elastic waves into the molten aluminum, the phenomenon of “cavitation” is caused in the molten aluminum, which destroys the continuity of the structure of the molten aluminum, and produces numerous microscopic vacuum holes, which are dissolved in the molten aluminum. Hydrogen quickly escapes into these cavities and becomes the core of the bubble. After it continues to grow up, it escapes out of the molten aluminum in the form of bubbles, thereby achieving a refining effect.