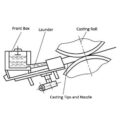
The vertical slab stage is the most critical moment of continuous casting and rolling production. Once the cast rolled vertical plate is successful, as long as the melt source is cut off, the casting and rolling can be carried out smoothly. At the beginning of the cast rolled vertical plate, the temperature fluctuation should be minimized when the temperature is required to ensure a certain fluidity of the melt. First of all, the melt temperature in the standing furnace should be controlled, generally stable at 740~750℃. The flow port can be opened, the melt is released, the flow trough and the front box are preheated with the melt heat, the waste melt used for preheating is discharged from the flow port behind the front box, and the melt temperature in the current box in the slag box reaches When the temperature is around 725℃, stay for a period of time. After the temperature has no obvious fluctuation, the operator confirms that everything is normal and prepares the vertical board.
First, plug the waste melt outlet behind the front box. When the melt fills the front box, open the graphite plug leading to the cross runner, so that the melt in the front box flows into the feeding pipe and supply under the action of static pressure. Feeding mouth, and quickly gushing from the feeding nozzle. The molten aluminum is taken away by the rotating casting roll, and the molten aluminum cooled into a semi-solidified state is shoveled into the slag box with a shovel. The slag running time is a few minutes, and the purpose is to use the melt heat to preheat the feed tube and the feed nozzle to make the melt temperature in the casting nozzle uniform and stable. At this time, pay attention to whether the melt temperature in the front box has a downward trend, which can be controlled by heating the melt in the launder with the burner.
Observe whether there is any abnormal phenomenon on the surface of the semi-solidified aluminum strip from the casting roll. For example, if there is a white bar, it means that the casting nozzle is blocked by inclusions, whether there are lumps, and the lumps are caused by the uneven temperature of the melt in the cavity of the feeding nozzle. Extending the slag run and preheating time can prevent such defects. At the same time, it is necessary to control the melt level of the front box. After everything is normal, the casting-rolling mill speed can be gradually reduced. While slowing down, carefully observe the board surface condition and the front box melt level. At this time, the front box melt temperature should reach the upper limit of the normal pouring temperature or slightly higher. After all the parameters meet the requirements, continue to reduce the speed to cast a shaped plate. When the plate enters the pinch roller, it can gradually increase the speed to bring out foreign matter such as moisture and glue. It is necessary to observe whether the edge of the solid strip is zigzag. This defect is caused by excessive gas in the melt. At this time, don’t rush to slow down to the tropics, keep it for a while, so that the gas can escape from the tropics.
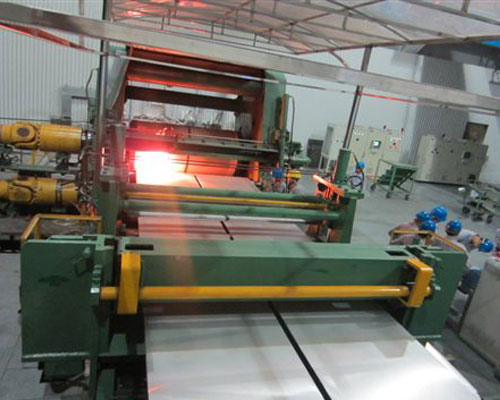

After the gas drops to a certain level, the casting speed should be appropriately reduced. Special attention should be paid to not because the front box melt level is high and the static pressure is large, so that the melt flows out of the gap between the feed nozzle and the casting roll. After the board surface is stable, adjust the process parameters and measure whether the board width is appropriate. Cut off the cast-rolled plate, take samples to check the thickness difference and crown value on both sides. Generally, the thickness difference on both sides should be controlled ≤0.02m, the crown value is between 0-1%, and the best value is between 0.4-0.5%. The grain size should be checked while the plate shape is adjusted. After all the indicators are qualified, the finished product can be coiled.