Metallurgy is to remove impurities (non-intentional elements) in the metal solution by melting (heating above the melting point) for slag formation and slag removal, while certain chemical components are relatively pure by slag removal, decarburization, deoxidation, etc. The process of alloy composition. The finer refining process for aluminium degassing treatment is generally a metal foundry.

Aluminium Degassing Treatment
Aluminium Degassing Treatment has always been the subject of research on aluminum alloy casting and rolling, and the purity of the nitrogen used for refining in the purification device is a key factor that directly affects the purification effect.
Aluminium Degassing Treatment is the purpose of spraying Nitrogen into molten aluminum to remove hydrogen. In addition, degassing is also considered to be a very effective way to float impurities.
Two main theoretical modes have been proposed to explain the principle of degassing. The macro mode considers that the removal of each impurity is similar in nature. The microscopic mode, that is, according to this theory, due to the higher vapor pressure of hydrogen, the dissolved hydrogen diffuses into the gas in the injected aluminum liquid.
Theoretically, an inclusion having a diameter of 10 microns contacts a bubble and is adsorbed on the bubble and floats up to the surface of the liquid.
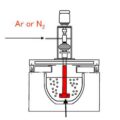
Aluminium Degassing Treatment breaks up the Nitrogen large bubble into a very fine small bubble by rotating the Nitrogen rotor at a high speed and uniformly disperses it in the molten metal.
By reducing the diameter of the bubbles, the total surface area of these bubbles increases sharply, which causes more Nitrogen bubble surfaces to come into contact with hydrogen and impurities in the molten metal to bring these harmful substances to the surface of the liquid.
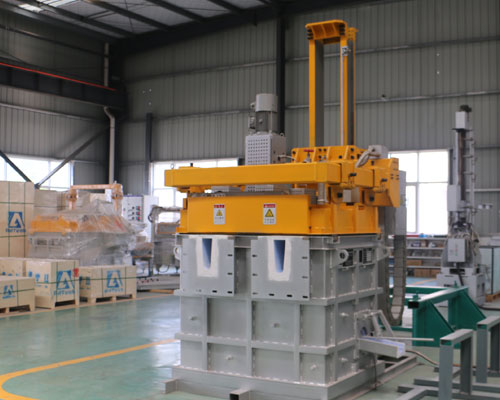

Aluminium Degassing
Aluminium Degassing Unit is that the rotor can break up the incoming Nitrogen bubbles into small bubbles and spread them throughout the molten metal.
By reducing the bubble diameter, the surface area of Nitrogen is drastically increased, so that more Nitrogen surface contacts the hydrogen and impurities in the molten metal and the hydrogen or impurities are removed from the aluminum liquid as the bubbles rise.
The flow control of the online degassing unit into the aluminum Nitrogen can adjust the flow rate of the gas according to the volume of the metal liquid being treated, and the speed of the rotating rod and the rotor can be adjusted to produce a bubble of an appropriate size to facilitate the diffusion of the inert gas.