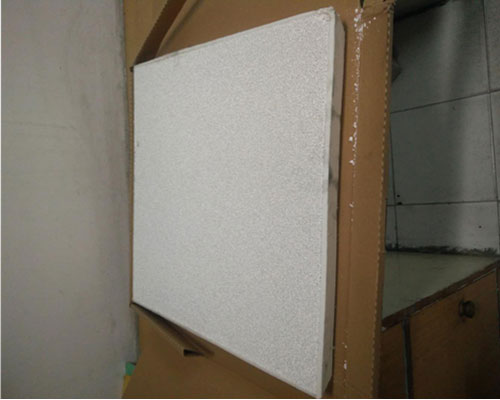

The aluminium casting ceramic foam filter includes a porous body having a plurality of end faces and an outer peripheral surface.
A ceramic foam filter is arranged on the inner wall of the main flow path of the filter box. Among them, the purification liquid flowing into the main flow path from the opening on the one end surface side is purified by the filter membrane and the porous interior.
Remove the purifying liquid from the outer peripheral surface of the porous body, or allow the purifying liquid flowing in from the outer peripheral surface of the porous body to pass through the inside of the porous body to purify the aluminum liquid, and remove it from the opening of at least one end surface of the main flow path.
Aluminum melt purification technology is the main subject of modern aluminum foundry research. The basic direction is to maximize the purification effect and improve the purity of the metal while preventing environmental pollution. During the aluminum smelting process, the oxide film is immersed in the melt. Some float on the surface of the aluminum melt or stick to the furnace wall. Those aluminum droplets and the surface of the melt are oxidized again, which also forms inclusions.
Once the inclusions are mixed into the cast-rolled strip, it will cause defects such as inclusions and oxide film. It greatly reduces the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of the product. Therefore, in the continuous casting and rolling process, the melt must be refined and purified to effectively reduce the content of gas and inclusions, and finally produce high-quality sheet and foil materials.
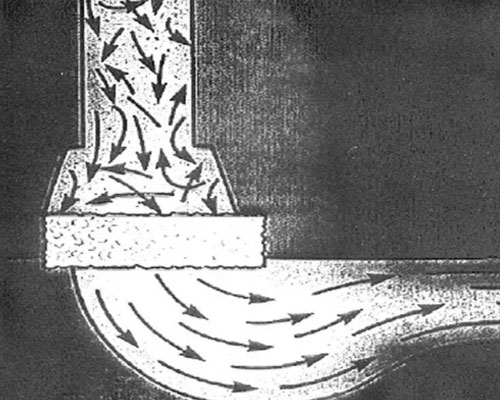
The aluminium casting ceramic foam filter is not only a mechanical barrier for inclusions, but also physical and chemical adsorption, micropores and chemical adsorption on the inner wall of the filter plate also promote the retention of inclusions. Therefore, the size of the filtered inclusions is much smaller than the size of the filter plate holes.
When filtering with a ceramic foam filter, in the initial stage, surface screening intercepts large particles, while small particles are removed by a deep filtration mechanism. As surface deposits form, the deposited layer can intercept large and small particles. And through the deep filtering mechanism to capture the fine inclusion particles in the mesh, the filtering effect of the filter plate will be better. When the adsorbed particles reach saturation, that is, when the number of particles adsorbed from the melt is equal to the number of particles carried away by the flowing melt, the slag removal ability decreases.





















