Alumina Molten Metal Filter can effectively remove a large amount of inclusions in the aluminum liquid, adsorb micron-sized fine inclusion particles, improve surface quality, improve product performance, improve microstructure and increase yield. It is widely used in the production of aluminum profiles, aluminum foil and aluminum alloys.
Understanding the basics of filtration and choosing the right filter media are essential for molten metal filtration.

Alumina ceramic foam filters have two main molten metal filtration modes, namely deep filtration and surface filtration. In the case of deep filtration, the particles are trapped inside the media; in surface filtration, they are retained on the surface where a particle cake is subsequently formed.
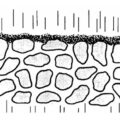
Surface filtration is mainly a filtration (sieving) mechanism in which particles larger than the pore size of the filter medium are separated on the upstream surface of the filter. Their size prevents them from entering or passing through the pore openings. Subsequent particles accumulate into lumps, and as more particle-laden fluid is forced into the filter medium, its thickness increases. Due to its potentially finer pore structure, the filter cake may help separate finer particles than the filter media can achieve.
However, the filter cake must have sufficient porosity to allow the filter cake to continue to flow during the filtration process. Since most surface filters do not have a completely uniform pore structure, some deep filtration may occur, which affects the life of the filter.
Depth filtration is mainly used for applications where the level of small particles must be separated. The particles penetrate the medium and are subsequently captured by its multilayer structure.
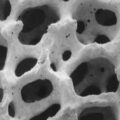
Understanding the filter’s ability to remove particles is the key to successful operation of the filter. For aluminum melt, filtering by trapping inclusions within the depth of the porous medium is the key to achieving a high level of efficiency. The Alumina Molten Metal Filter has a three-dimensional porous structure, it provides a tortuous path for trapping particles.