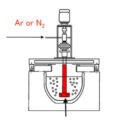
On-line degassing process is a hydrogen removal process carried out at the same time in the casting process. Since the molten aluminum undergoes hydrogen removal in the holding furnace, the molten aluminum enters the casting machine through the launder and is in contact with air. It can still absorb hydrogen again, resulting in the hydrogen content in the aluminum liquid exceeds the required index. Therefore, On-line Degassing Process is necessary to minimize the hydrogen content in the molten aluminum.

Hydrogen is the only gas that can be dissolved in molten aluminum in large amounts. According to the traditional aluminum liquid refining system for the hydrogen dissolved in the aluminum liquid, through the physical adsorption of the inert gas Ar, the nitrogen bubbles float in the aluminum liquid while adsorbing the hydrogen in the aluminum liquid, so that the aluminum liquid is purified.
There are many factors influencing the on-line degassing process of molten aluminum, mainly including: atmospheric humidity, inlet molten aluminum hydrogen content, molten aluminum temperature, alloy condition, refined gas purity, refining time, contact area of bubbles and molten aluminum, etc. The impact status is as follows:
Atmospheric humidity: The source of hydrogen in molten aluminum is mainly due to the reaction between molten aluminum and water vapor. If the atmospheric humidity is high, the water vapor content in the atmosphere is high, and the hydrogen content formed after the reaction with the aluminum liquid increases, and the difficulty of the hydrogen removal process increases. [H generated by the reaction exists in the aluminum liquid in an atomic state, or exists on the grain boundary. If the hydrogen cannot be effectively removed, after the aluminum liquid solidifies, the hydrogen will cause pores, looseness and other defects in the cast product. Hydrogen on the grain boundary easily leads to the hydrogen embrittlement of the cast product, which affects the mechanical properties of the product. If there is water or steam in the molten aluminum launder and the crystallizer, the above chemical reaction will also occur, forming hydrogen, and dissolving into the molten aluminum.
The hydrogen content of the liquid aluminum: When using the inert gas rotating injection refining device, according to the conclusion of the research on the hydrogen removal kinetics of the liquid aluminum, the lower the hydrogen content of the inlet liquid aluminum, the lower the hydrogen removal efficiency, and the more difficult the hydrogen removal process. When the hydrogen content of the inlet liquid aluminum is less than 0.300m1/100g, for AA5182 alloy, the hydrogen removal efficiency can reach about 50%.

Temperature of molten aluminum: The temperature of molten aluminum will affect the reaction of molten aluminum with water vapor in the atmosphere. The higher the temperature of molten aluminum, the greater the degree of reaction between molten aluminum and water vapor, and the corresponding increase in hydrogen content in molten aluminum. At the same time, the temperature of the molten aluminum will affect the density of the surface oxide film. If the temperature of the molten aluminum is too high, the oxide film on the surface becomes loose, and the water vapor in the atmosphere easily penetrates the oxide film to react with the molten aluminum, which increases the hydrogen content in the molten aluminum.
The hydrogen content in different alloy aluminum liquid is different. The influence of the alloy on the hydrogen content of the molten aluminum is mainly through the influence of the density of the oxide film on the surface of the molten aluminum. If the alloy elements contained in the molten aluminum will cause the oxide film to become loose, the hydrogen content in the molten aluminum will increase. The Mg content in the AA5182 alloy is 4.0%-5.0%. Mg will cause the oxide film to become loose. The water vapor in the air easily penetrates the oxide film into the aluminum liquid, and reacts with the aluminum liquid to increase the hydrogen content, so the AA5182 alloy aluminum liquid hydrogen The content is relatively high, and the online degassing device needs to be optimized so that the hydrogen content of the aluminum liquid can be reduced to below 0.150m1/100g.
Purity of refined gas: The refined gas is mainly inert gas, among which Ar is the main component, and a certain proportion of Cl2 is mixed. The role of Cl2 is mainly to remove alkali metals and alkaline earth metals in molten aluminum. The main effect of the purity of the refining gas on the hydrogen removal process of the molten aluminum is: the refining gas enters the molten aluminum, and the water vapor in it will react with the molten aluminum to produce hydrogen. While removing hydrogen, the water vapor in the Ar will cause the molten aluminum. The increase in hydrogen content affects the refining effect. The water vapor in Cl2 will have the same effect.
Refining Time: Within a certain range of refining time, the longer the refining time, the greater the amount of hydrogen permeating into the inert gas bubbles. But after a certain period of time, with the extension of refining time, the effect of hydrogen removal does not change significantly.

The contact area between the inert gas bubble and the aluminum liquid: in the process of floating in the aluminum liquid, the inert gas bubble absorbs the hydrogen in the aluminum liquid. After the hydrogen atoms enter the inert gas bubble, they combine with each other to form H2, and float to the surface of the aluminum liquid with the inert gas bubble. The H2 is released to complete the process of removing hydrogen from the molten aluminum. In order to improve the hydrogen removal effect of molten aluminum, the larger the total contact area between the inert gas bubbles and the molten aluminum, the better the hydrogen removal effect. In order to increase the total contact area between the inert gas bubbles and the molten aluminum, the inert gas needs to be broken up as much as possible to become fine bubbles. With the inert gas flow rate constant, the total contact area between the bubbles and the molten aluminum can be increased.
Through the high-speed rotation of the graphite rotor, the bubbles can be crushed. But the rotation speed of the graphite rotor cannot be increased intentionally. If the rotation speed is too high, it is easy to form a vortex on the surface of the molten aluminum, which will destroy the oxide film on the surface of the molten aluminum and mix the oxide inclusions into the molten aluminum, causing the molten aluminum to be contaminated. The content of oxide inclusions in the molten aluminum increases while the hydrogen content increases.
Among the above factors that affect the refining effect of on-line degassing process, in addition to natural conditions and fixed equipment conditions, the main factors that can be optimized include: one is the preheating of the process gas, and the other is the matching of the bubble expansion degree and the geometric size of the degassing box. By optimizing these two factors, the total area of contact between bubbles and molten aluminum can be increased, and the hydrogen removal effect can be improved.